Curious about the ray reconstruction feature being introduced on PC with DLSS 3.5? Today, I’ll be discussing ray reconstruction and all you need to know about the feature, including what GPUs can actually use it with. Before diving too deep into ray reconstruction, we’ll take a few moments to discuss ray tracing and related technologies so the explanation of ray reconstruction makes a little bit more sense, too. You can skip around instead if you like, though!
Table of Contents
Real-Time Ray Tracing: A Brief
So, what is real-time ray tracing? Let’s break it down.
“Real-time” just means that frames are immediately presented to you as they are rendered, and of course any game is technically a real-time application. (Not to be confused with real-time strategy.) Ray-tracing is pretty intensive, though, so that “real-time” qualifier is important and requires dedicated onboard hardware to perform.
Ray tracing is a little more complicated to explain, but let’s start by just talking about the dynamics of light. Rays of light bounce, reflect, and refract in accordance with what environment they pass through in real life. Ray tracing is all about simulating rays of light and how they interact with the environment with higher degrees of accuracy, allowing for more realistic reflections, global illumination, and shadows.
Reflections are a major example. Modern titles without ray tracing tend to rely on a technique called SSR (Screen Space Reflections) in order to provide reflections to the user. However, a “Screen Space” effect is going to be limited to what’s actually in view of the player’s camera at the time, resulting in many expected viewing angles being simply not visible, or “faked” with static cubemaps. A “Ray Traced” effect is not limited by Screen Space at all, allowing for accurate reflection and lighting from offscreen objects.
What is Ray Reconstruction?

So, what is ray reconstruction?
Ray reconstruction is a new feature being added to Nvidia RTX GPUs that leverages Tensor AI cores with RT cores in order to improve the ray tracing quality and performance, especially path traced titles. Specifically, ray reconstruction uses AI to implement upscaling directly into the ray tracing rendering pipeline, allowing for far higher-quality ray traced effects without the need for an otherwise-required denoiser.
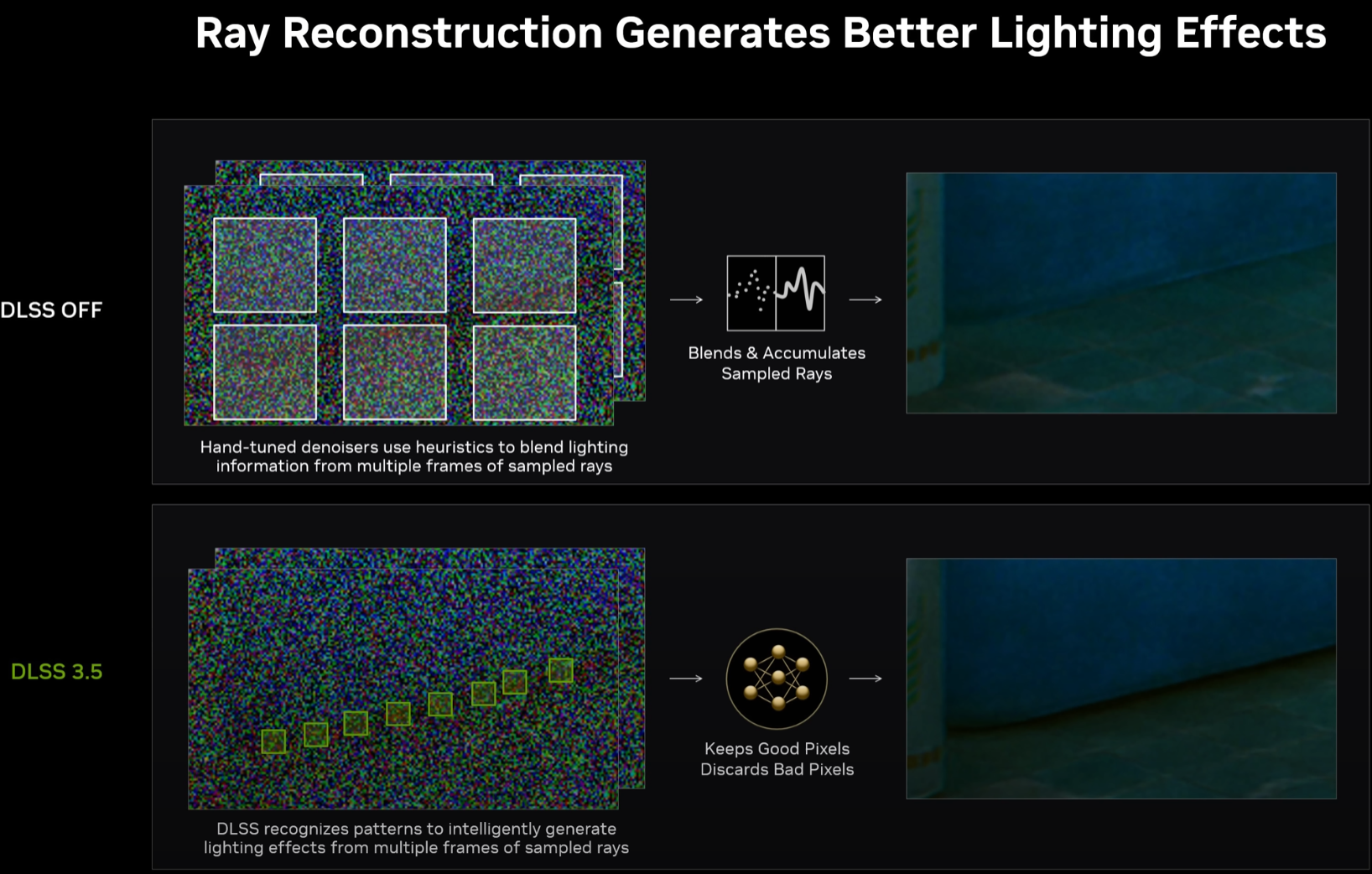
What is DLSS 3.5?
DLSS 3.5 is the version of Nvidia’s DLSS that ray reconstruction is being introduced with. It is primarily being marketed around this feature, since it greatly improves the quality of ray traced effects and can more readily be worked into the upscaling pipeline already typical when running ray traced games.
While DLSS 3.5 is the latest version of DLSS, it offers varying levels of support for all RTX GPUs, unlike the Frame Generation feature of DLSS 3, though it improves upon that feature’s performance on newer cards as well.
Does DLSS 3.5 Work On Older RTX GPUs?
DLSS Frame Generation, which does considerably improve framerate in ray traced titles, still isn’t supported on RTX cards prior to the 40 series. However, all RTX cards do support ray reconstruction as long as the game in question does, so a limited form of DLSS 3.5— with reconstruction but not frame generation— should always be present!

Will AMD GPUs Implement Ray Reconstruction?
Probably not, unfortunately. AMD don’t seem interested in introducing AI chips to their GPUs, at least not at the time of writing. However, the dramatic improvement to visual quality offered by using dedicated AI cores in the ray tracing pipeline might just be the push AMD needs to reconsider. Who knows?

